Types of Pallet Racks Used in a Warehouse
Pallet racks bring structure, stability, and efficiency to warehouses and distribution centers. All contain basic components such as upright frames and beams, but that is where the similarities end. These varied systems are wonderfully versatile and capable of meeting many unique material handling needs.
While this variety can be appealing, it may also prompt confusion: it can be difficult to know which pallet racking types are most desirable in any given situation. There is no easy way to make this decision, but it may help to examine the many options available.
To that end, we have compiled a thorough guide to today's most popular pallet racking and shelving types, highlighting associated benefits, challenges, and use cases.
Understanding Pallet Racking Systems
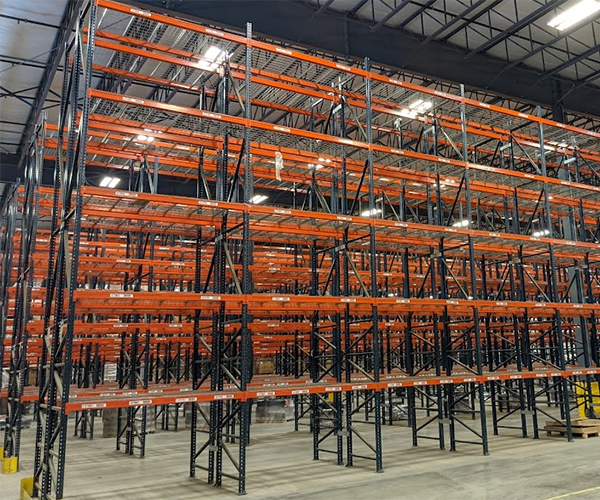 Before we delve into the differences between various pallet racking systems, it is important to understand what links these many pallet racking setups. These material handling solutions organize pallets in rows and multiple levels.
Before we delve into the differences between various pallet racking systems, it is important to understand what links these many pallet racking setups. These material handling solutions organize pallets in rows and multiple levels.
Pallet racking systems strive to maximize warehouse space while also promoting accessibility. The degree to which these priorities are pursued could vary based on the types of products stored and according to the size and layout of the warehouse.
Looking to shop pallet racking? See WH1’s new and used pallet racks for sale.
Pallet Racking Types
Pallet racking is more diverse and more complicated than many people realize. Different warehouses and distribution centers have dramatically different needs, but these can easily be accommodated by various pallet racking setups.
Each arrangement offers unique benefits and challenges—and some pallet racks may not be realistic for certain types of warehouses. In most cases, however, warehouses will feature at least one of the pallet racking solutions highlighted below:
Selective Pallet Racking
 Common in many warehouse settings, selective pallet racking offers direct access to all pallets. This often involves single-deep configurations in which every pallet is visible and, therefore, accessible.
Common in many warehouse settings, selective pallet racking offers direct access to all pallets. This often involves single-deep configurations in which every pallet is visible and, therefore, accessible.
Pros
As one of the most cost-effective pallet racking types (at least from an installation and maintenance standpoint), selective racking is an easy choice for a wide range of warehouse applications. It is versatile, easy to install, and, as its name implies, highly selective. This drives easy and efficient inventory retrieval.
Cons
If storage density is a priority, selective racking may not be the best choice. This can be problematic when dealing with smaller warehouses or for high-volume operations. Installation costs may be low, but the cost per pallet position may actually be higher than for different types of pallet racking.
Factors to Consider
Highly versatile, selective racks accommodate FIFO (first-in, first-out) and LIFO (last-in, first-out) setups. Main factors include funding available for installation, along with available warehouse space and product volume.
Double Deep Pallet Racking
 Offering higher storage density than typical selective solutions, double deep systems place pallets two deep—one pallet situated directly behind the other. Specialized forklift equipment may be required.
Offering higher storage density than typical selective solutions, double deep systems place pallets two deep—one pallet situated directly behind the other. Specialized forklift equipment may be required.
Pros
Double deep arrangements feature many benefits associated with selective racking but also the chance to overcome common concerns related to storage density. These systems offer selective access but can lead to long-term savings by reducing the warehouse's overall footprint.
Cons
Compared to selective racking, double deep is far more difficult to implement. Accessibility may be limited for pallets situated at the back of each rack. Selectivity is still possible but not as strong with double deep setups.
Factors to Consider
Like selective racking, double deep systems support both LIFO and FIFO. This is an ideal approach when storage density is a priority but also when some element of selectivity remains important.
Drive-In Pallet Racking
 Best known as a high-density solution, drive-in pallet racking involves deep storage lanes in which vehicles can drive in to access stored products. These pallets can be situated several positions deep, with aisles avoided between rows of racks.
Best known as a high-density solution, drive-in pallet racking involves deep storage lanes in which vehicles can drive in to access stored products. These pallets can be situated several positions deep, with aisles avoided between rows of racks.
Pros
Offering a potential alternative to warehouse expansion, drive-in pallet racking delivers extraordinarily high storage density—arguably the highest capacity of any conventional pallet racking method. This produces a uniquely low cost per pallet position, making drive-in one of the most cost-effective options on a long-term basis.
Cons
Although drive-in racking produces amazing storage density, selectivity suffers as a result. Pallets may need to be moved out of the way, thereby leading to time-consuming retrieval efforts. Damage from forklift impact is also possible, as this setup requires vehicles to drive into the racking structure.
Factors to Consider
Many enterprises seek to avoid LIFO arrangements, which is a component of drive-in racking. It is usually most suitable when high volumes are involved. It works best for limited SKUs and also for limited turnover situations.
Drive-Through Pallet Racking
 Featuring distinct entry and exit points, drive-through pallet racking allows for the efficient movement of inventory and can promote impressive throughput. Pallet racks can be accessed from both sides, but storage remains relatively dense.
Featuring distinct entry and exit points, drive-through pallet racking allows for the efficient movement of inventory and can promote impressive throughput. Pallet racks can be accessed from both sides, but storage remains relatively dense.
Pros
Drive-through racking offers decent storage density while addressing common concerns associated with drive-in systems: accessibility and congestion. With these issues eliminated, expedited rotation is possible.
Cons
Design complexity can make drive-through systems feel intimidating. They take far more effort to install and implement, especially as extra safety features and training may be required. Support capacity may reduce the total load capacity and, depending on inventory levels, congestion remains possible.
Factors to Consider
Because it so clearly aligns with the FIFO method, drive-through pallet racking is at its best when stock rotation is a priority. As such, it can be a viable solution for dealing with perishable goods. It may not be as ideal when strict space limitations exist.
Push Back Pallet Racking
 Leveraging rails to move pallets, push back racking offers a unique solution for high-density operations, storing several pallets deep. These systems feature rollers or shuttles, with pallets loaded by forklifts. The name derives from the need to push the first pallet back and then continue pushing pallets back until the last one has been loaded.
Leveraging rails to move pallets, push back racking offers a unique solution for high-density operations, storing several pallets deep. These systems feature rollers or shuttles, with pallets loaded by forklifts. The name derives from the need to push the first pallet back and then continue pushing pallets back until the last one has been loaded.
Pros
It can be difficult to find pallet racking systems that maintain high storage density and selectivity, but push back racking accomplishes both objectives. Forklifts need not enter the storage lane, so the potential for damage is greatly reduced. This can be a highly efficient setup that allows for space optimization.
Cons
Wheeled carts and inclined rails add complexity to push back systems, which, as a result, may be more expensive and time-consuming to implement. Selective access can be a perk, but these systems are not as accessible as conventional selective racks. Load-bearing capacity may also be a concern for deeper pallet positions.
Factors to Consider
Often implemented for LIFO operations, push back systems may be less ideal for some perishable goods. This system is at its best when there is a reduced need for picking and when compatibility is required to accommodate multiple storage solutions.
Pallet Flow Racking
 As a dynamic system best known for its strategic use of rollers, pallet flow racking involves a precise system in which pallets are loaded on one side and then allowed to 'flow' to the other. Pallets can continue to accumulate until the racking system has reached its maximum capacity. Pallets can then be removed from designated unloading areas.
As a dynamic system best known for its strategic use of rollers, pallet flow racking involves a precise system in which pallets are loaded on one side and then allowed to 'flow' to the other. Pallets can continue to accumulate until the racking system has reached its maximum capacity. Pallets can then be removed from designated unloading areas.
Pros
Ideal for high-volume arrangements, pallet flow racks provide a unique blend of high-density storage and efficient product turnover. Separating loading and unloading can be advantageous, as this allows for a seamless flow within the warehouse environment and enables forklift drivers to work without interruption.
Cons
Pallet flow racks tend to be complicated to design and implement. Although these systems are cost-effective in the long run, the initial investment may be higher than expected.
Factors to Consider
Pallet flow racking is preferable for FIFO setups, with the oldest inventory unloaded first. This can be valuable for avoiding spoilage and, in general, is a preferred setup when both high volumes and high turnover are anticipated.
Cantilever Racking Systems
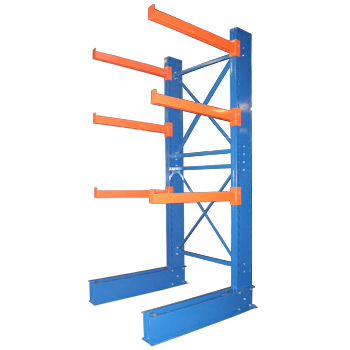 Visually distinct from the pallet racking systems described above, cantilever racking replaces conventional shelving or wire decking with load-carrying arms. These are designed to handle large or unusually shaped items that cannot be accommodated by conventional pallet racking solutions.
Visually distinct from the pallet racking systems described above, cantilever racking replaces conventional shelving or wire decking with load-carrying arms. These are designed to handle large or unusually shaped items that cannot be accommodated by conventional pallet racking solutions.
Pros
With some products, cantilever racking is the only realistic setup, as it can accommodate a wide range of shapes, sizes, and styles. Modular designs can be implemented to further enhance versatility.
Cons
Often more expensive to install than selective racking, cantilever styles may provide reduced storage density and throughput. This approach is only desirable if typical pallet racking cannot realistically accommodate unusually shaped products.
Factors to Consider
Cantilever racking maintains specific use cases: it's the last resort option when other pallet racking types are ill-suited to storing uniquely shaped products. Often, this setup is preferred for storing lumber or furniture that cannot be kept on the floor.
Carton Flow Rack
 Featuring a slight incline along with rollers, carton flow racks provide yet another opportunity to make the most of gravity within the warehouse environment. This setup is often developed in hopes of making picking easier and more efficient.
Featuring a slight incline along with rollers, carton flow racks provide yet another opportunity to make the most of gravity within the warehouse environment. This setup is often developed in hopes of making picking easier and more efficient.
Pros
Promising to boost productivity, carton flow racks are advantageous for picking operations, as these systems make it easier for pickers to retrieve items. These systems are versatile; they work wonderfully when small items are stored in cartons but can also handle larger boxes.
Cons
As with other dynamic solutions, carton flow racks can sometimes be expensive to design and install. Maintenance complications can also be expected. Some larger items may not be well-suited to these systems.
Factors to Consider
Preferable for FIFO arrangements, carton flow racks are commonly used in warehouses that store food and beverage products. These racks are also frequently found in eCommerce distribution centers.
Specialized Racking Solutions
The pallet racking systems highlighted above accommodate a range of enterprises and boast numerous use cases. Still, some businesses may call for setups that are even more specialized. Examples include:
Cold Storage
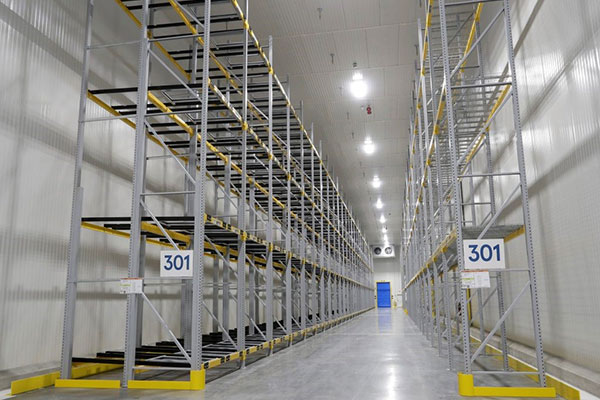 Cold storage racking systems must provide strong temperature and humidity monitoring, along with strategic solutions to boost throughput. Operational expenses can escalate dramatically, so exceptional space utilization is essential.
Cold storage racking systems must provide strong temperature and humidity monitoring, along with strategic solutions to boost throughput. Operational expenses can escalate dramatically, so exceptional space utilization is essential.
FIFO arrangements are generally preferred, with pallet flow racking, in particular, working wonders for frozen storage. In some situations, however, push back racks can also get the job done.
High-Density Storage Solutions
Many modern warehouses and distribution centers have high-volume needs that can only be accommodated by a few specific types of pallet racking. Drive-in racking systems are best known for their elite storage density, although some push back racks and even double-deep racks accommodate high volumes.
Narrow Aisle Racking Systems
Ideal for warehouses with limited space, racking systems with narrow aisles make it possible to dedicate more room to storing products. These may complicate forklift operation, but access can be maintained with a specific setup: Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) pallet racking. Specialized forklifts are required, but this makes it possible to reduce aisle sizes to a mere six feet.
Key Considerations
There is a lot to consider when selecting or developing a pallet racking system. Competing priorities may come into play, and depending on budgetary realities, some compromises may be required. Top factors to examine include:
Storage Capacity
 Pallet racking capacities can vary dramatically, but some systems are purposefully designed to deliver maximum storage capacity. Capacity guidelines must be strictly followed to ensure the long-term integrity and safety of pallet racking systems.
Pallet racking capacities can vary dramatically, but some systems are purposefully designed to deliver maximum storage capacity. Capacity guidelines must be strictly followed to ensure the long-term integrity and safety of pallet racking systems.
Warehouse Space and Configurations
Smaller warehouses may not accommodate certain pallet racking configurations. Every square foot must be used strategically, with aisle space ideally minimized to free up more room for inventory.
Material Handling Equipment
Some pallet racking systems call for specific equipment, including specialized forklifts. Some even accommodate cutting-edge solutions such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs). This equipment can boost efficiency or space utilization, but the initial investment is significant.
Durability and Functionality
Pallet racking should be a long-term investment, so highly durable systems are always preferred. This is especially important for pallet racks that are vulnerable to forklift impact. Steel pallet racks are extremely durable, and features like column guards can further help these racks stand up to general wear and tear.
Best Practices
Industry-specific considerations and objectives must be top of mind when selecting pallet racking. What works well for one type of warehouse could cause huge problems elsewhere. Other best practices to keep in mind include:
- Careful planning, pre-installation, and installation procedures will ensure that pallet racks are safe and functional.
- Make the most of components such as wire decking and teardrop fasteners, which can enhance many pallet systems.
- Work with a professional to design and install pallet racking systems — or to assist with relocation or reconfiguration.
Choose Warehouse1 for Your Pallet Racking Needs
There is no easy solution when it comes to pallet racking. Because these play such a vital role in shaping warehouses and facilitating seamless workflows, they must be selected carefully and according to enterprise-specific concerns.
Struggling to select the right warehouse storage system or pallet racking solution? Look to the experts at Warehouse1 for insight. We offer many types of pallet racks and accessories, along with design, installation, and repair services. Reach out today to learn more.



